The bitter gourd, also called karela in Hindi, is a vegetable with a taste that matches its name. It is extensively consumed all throughout the world, but Asians are its biggest consumers. Like most vegetables, bitter gourds can also be infested with various diseases that can cause significant yield losses if not managed well. Major bitter gourd diseases include Powdery Mildew, Downy Mildew, Angular Leaf Spot, and Mosaic Disease. Let’s understand these diseases in detail, including an understanding of their symptoms, and the effective pest management methods to control them.
1️⃣Powdery Mildew
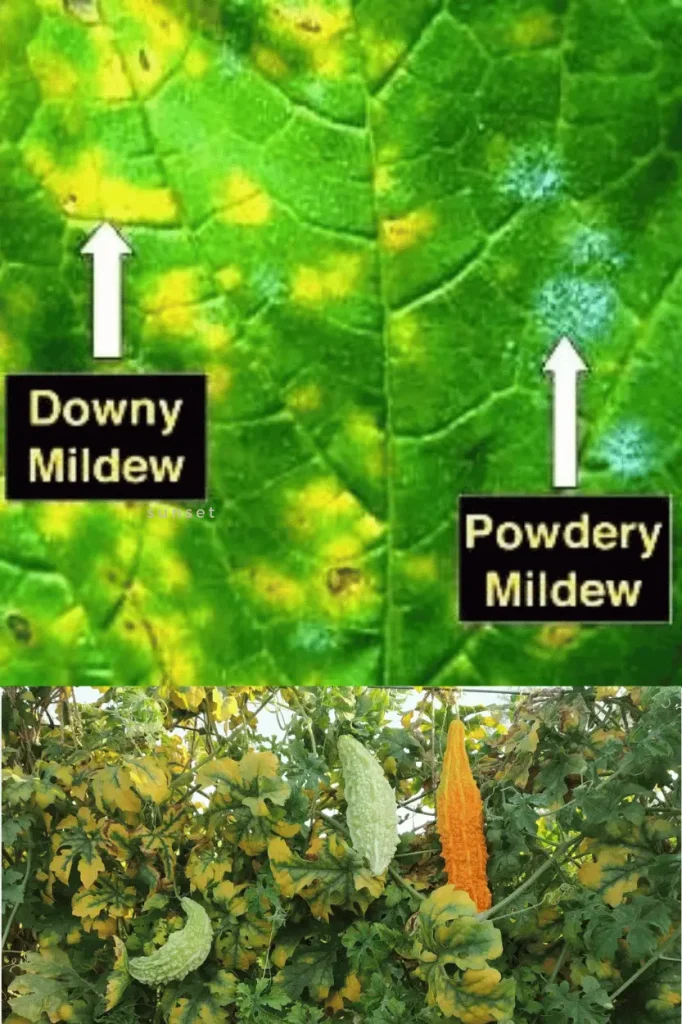
Powdery mildew is one of the common fungal diseases in bitter gourd farming. It is mainly caused by the fungus Podosphaera xanthii. It mostly happens in a warm and humid farming condition and spreads quickly among the plants. The first sign of powdery mildew is pale yellow leaf spots. Later, we will see a few white powdery spots that can form on both upper and lower leaf surfaces. Let us see what the common symptoms of bitter gourd powdery mildew disease are.
How to Identify Powdery Mildew in Bitter Gourd
- White powdery residue on the upper surface of leaves, stems, and other growing parts.
- Leaves may turn yellow or brown, especially in areas with heavy fungal growth.
- Leaves eventually dry out and fall off.
- Infected leaves may shrivel and become misshapen.
- Stunted growth due to decreased photosynthesis.
- Infected plants may produce smaller and less flavourful fruit.
- In severe cases, powdery growth may cover the entire plant, causing it to plant death.
Effective Management of Powdery Mildew
- Provide good air movement around plants through proper spacing, staking of plants and weed control.
- Use fungicides: Tebuconazole 25.9% EC on a ratio of 1 ml/lit water, Hexaconazole 5 % EC on a ratio of 2 ml/lit water.
- Apply fertilizer based on soil test results. Avoid over-applying nitrogen.
2️⃣Downy Mildew
Downy mildew is a common disease in bitter gourd farming caused by the fungus Pseudoperonospora cubensis. It develops in cool, moist conditions and can spread rapidly in humid environments. The first sign of downy mildew is pale green to yellow spots on the upper surface of leaves, which later turn brown. Let us see what are the common symptoms of bitter gourd’s Downy Mildew disease.
How to Identify Downy Mildew in Bitter Gourd
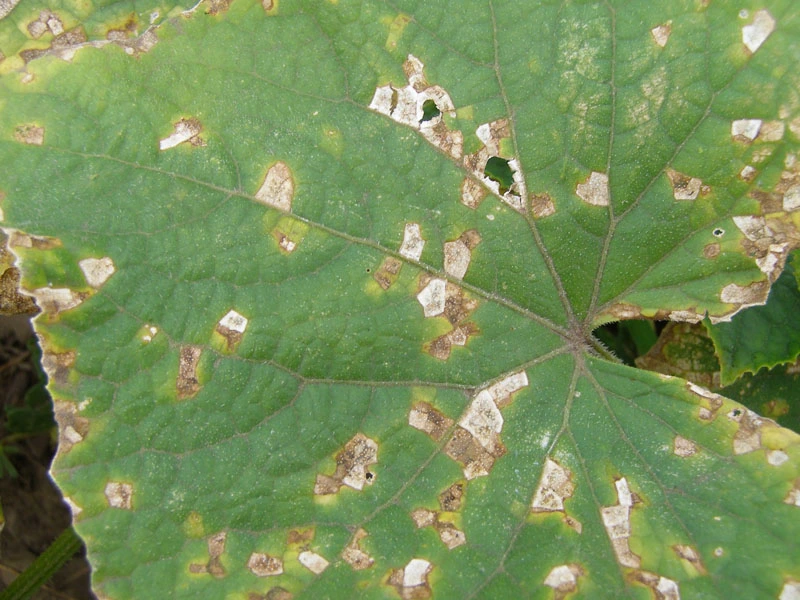
- Pale green to yellow spots on the upper surface of leaves, turning brown later.
- Brown spots develop on infected leaves, often with a yellow halo as the disease progresses.
- Fuzzy grayish-white water-soaked lesions appear on the underside of leaves in moist conditions.
- Causes rapid leaf drop (defoliation).
- Rapid defoliation of affected leaves.
- Stunted growth in affected plants, leading to plant death in severe cases.

Effective Management of Downy Mildew
- Provide good air movement around plants through proper spacing, staking, and weed control.
- Use drip irrigation and wide row spacing to dry the leaves and encourage good air movement.
- Trellis (provide frames) plants to improve air circulation.
- Remove plants with symptoms of the disease.
- There are no effective pesticide products for downy mildew available to home gardeners.
- Apply fungicide:
- Metiram 55% + Pyraclostrobin 5% WG: 1 gm/lit water
- Metalaxyl 4% + Mancozeb 64% WP: 1.5 gm/lit water
- Chlorothalonil 75% WP: 2.5 gm/lit water
There are resistance concerns around downy mildew, so make sure to follow labels carefully and rotate products while using fungicide.
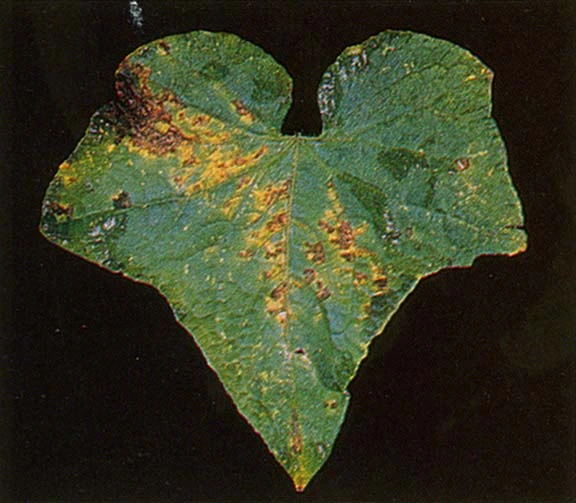
3️⃣Angular Leaf Spot (Bacterial Disease in Bitter Gourd)
Pseudomonas syringae pv. lachrymans causes the bacterial disease known as angular leaf spot. The pathogen can survive in plant debris for over two years. When humidity is high, a drop of clear to white sticky bacterial ooze forms on infections. These bacteria move from plant to plant on the hands and tools of workers, by insects, or by splashing water. When bacteria infect the fruit, it moves deep into the fruit and infects the seed. Contaminated seed can introduce the disease into a field.

How to Identify Angular Leaf Spot in Bitter Gourd
- Leaves develop small, angular, brown or straw-coloured spots with a yellow halo.
- Leaf spots dry and drop out, leaving irregularly shaped holes in the leaves.
- The spots typically remain within the leaf veins.
- Water-soaked tan, small circular spots on fruit.
- Bacterial soft rot often develops after fruit spots and rots the entire fruit.
- Sticky drops of whitish liquid form on the underside of the leaf when wet, drying to a crust when dry.
Effective Management of Angular Leaf Spot
- Rotate vegetables so two or more years go by before planting any member of the squash family in the same location.
- Use drip irrigation instead of overhead sprinklers if possible.
- Buy clean seed from a reputable source. If saving seed, do not collect seed from infected plants. Hot water treatment can remove some, but not all, bacteria.
- Infected seeding material can be treated with garlic solutions and hot water (50°C) for 30 minutes.
- In greenhouses, the occurrence of angular leaf spot can be suppressed by controlling night-time humidity (to 80-90%) with dehumidifiers.
- Pesticides containing copper hydroxide can be applied. The treatment is most effective when the temperature is above 24°C and the foliage is wet.
- Spraying on a hot day when the foliage is dry can injure the plants.
- Weekly spraying may be necessary to achieve control of the disease.
- Use fungicides Copper Oxychloride 50% WP: 2 gm/lit water or Kasugamycin 3% SL: 2 gm/lit water
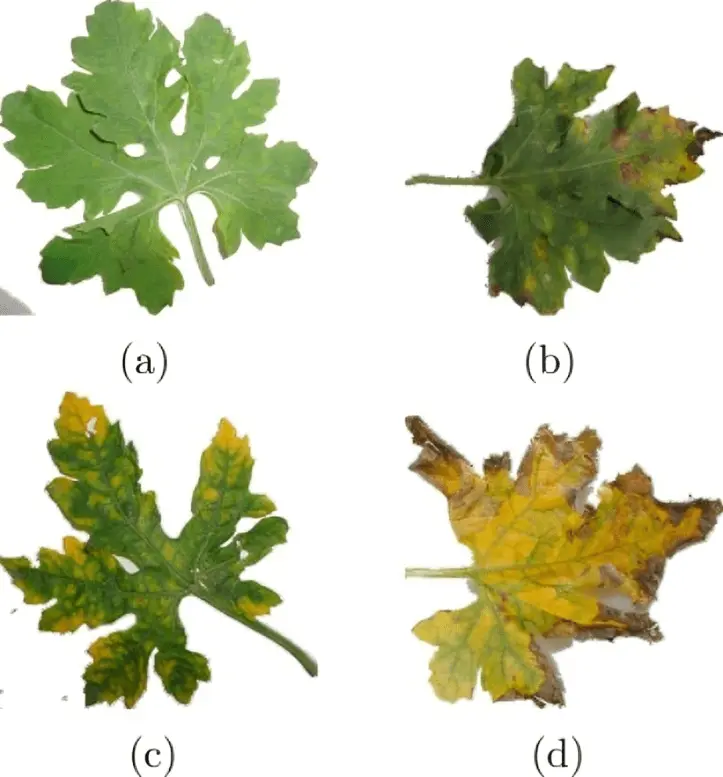
4️⃣Bitter Gourd Yellow Mosaic Virus Disease
Bitter gourd Yellow Mosaic Virus (BGYMV) is a whitefly-transmitted gemini virus that causes yellow mosaic disease in bitter gourd. This disease is significant because the virus can attack the crop at all stages, leading to severe yield loss, and it’s also one of the most fatal bitter gourd diseases. BGYMV has been reported to infect bitter gourd naturally, causing enormous losses in terms of yield and fruit quality.
How to Identify BGYMV in Bitter Gourd
- Yellow mosaic patterns on leaves.
- Leaves become distorted and curled.
- Stunted plant growth.
- In severe cases, the disease affects the entire plant, leading to its death. Sometimes, it also reduces fruit quality and yield.
Effective Management of BGYMV Disease in Bitter Gourd
- Choose resistant or tolerant cultivars to reduce the risk of disease outbreaks. Several resistant varieties have been developed and are effective against YMV infection.
- Treat seeds with fungicides or hot water treatment (50°C for 30 minutes) to eliminate potential viruses.
- Chemical control measures are limited but can include antiviral chemicals like Actara and Mating Disruption Technique to reduce virus transmission.
- Use insecticides like Imidacloprid to control whitefly populations.
- Apply chemicals like:
- Actara 25% WG: 1 gm/lit water
- Bougainvillea spectabilis extract: 10% w/v for inducing resistance
- Salicylic acid: 2.5 mM for effective disease resistance
By implementing these management strategies, farmers can mitigate the impact of BGYMV and improve bitter gourd production, ensuring a profitable and sustainable cultivation.
Before applying pesticides and starting pest control measures, it’s important to ensure your plants are healthy. Healthy plants are more resilient and can better withstand disease pressures.
Read our 4 cost saving tips to ensure your plants are growing in fertile soil.
Managing bitter gourd diseases like Powdery Mildew, Downy Mildew, Angular Leaf Spot, and Yellow Mosaic Virus is crucial for healthy crops. Follow these management strategies to protect your plants and boost your yield. However, always consult an expert before applying any chemicals.
Want to order these pesticides for your field? Looking for free crop advisory services?